Inspecting Structural Insulated Panels (SIP)

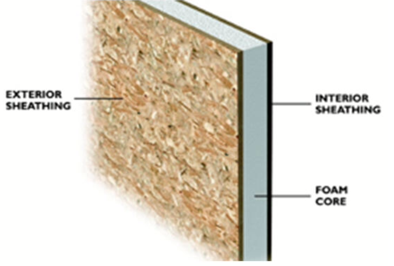
| Structural Insulated Panels (SIP) are building panels used in residential and commercial buildings that consist of panels of insulated foam sandwiched between two structural facings. The facings typically are (Oriented Strand Board) OSB. However plywood could be used. These large panels are manufactured in a factory to exact specifications and shipped to the building site where they are assembled. SIPS construction is different than normal framing because of the way the panels are constructed; they actually are the structure. There are many differences. Foundation straps are used to secure the panels instead of sill bolts. Panel corners and roof to wall connections are screwed together. Special fasteners are used to attach porch roofs to SIPS buildings. Floor joists are attached with a top chord bearing hanger that is attached to the top of the SIPS panel. A ridge beam and possibly a mid span beam may be used to support the roof panels. Here is a video of a SIPS house being constructed: https://youtu.be/liTV_iLkdl0.
What should a home inspector should be looking for?
Related Articles: |
- Inspecting Light Fixture Type & Location
- EIFS – Additional Inspection Guidelines
- Smoke & Heat Detector Placement: How To Properly Advise Your Clients
- Looking For Back Draft
Want To Learn More? Click HERE to Search Our Full Database Of Home Inspector Newsletters.



